Log All
Overview
- You will create a new rule in Amazon EventBridge.
- You will test the new rule and see the input payloads.
- You will configure the new rule to log all events to Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
Each Serverlesspresso event is emitted to a custom event bus named “Serverlesspresso”.
An event is a change in state, or an update, like an order being placed on the customer website. Events can either carry the state (the item ordered, its modifiers, and user id) or events can be identifiers (a notification that an order was completed).
Event-driven architectures have three key components: event producers, event routers, and event consumers. A producer publishes an event to the router, which filters and pushes the events to consumers. Producer services and consumer services are decoupled, which allows them to be scaled, updated, and deployed independently.
Events are ephemeral in nature, meaning that they are not stored when received. It’s often useful to log events and their state for later inspection and playback.
Creating the “Log All” rule
Create a rule that logs every event through the application’s custom bus to CloudWatch Logs.
Step-by-step instructions
-
Go to the EventBridge console. From the AWS Management Console, select Services then select EventBridge Application Integration. Make sure your region is correct.
-
Choose Rules. Choose Create rule.

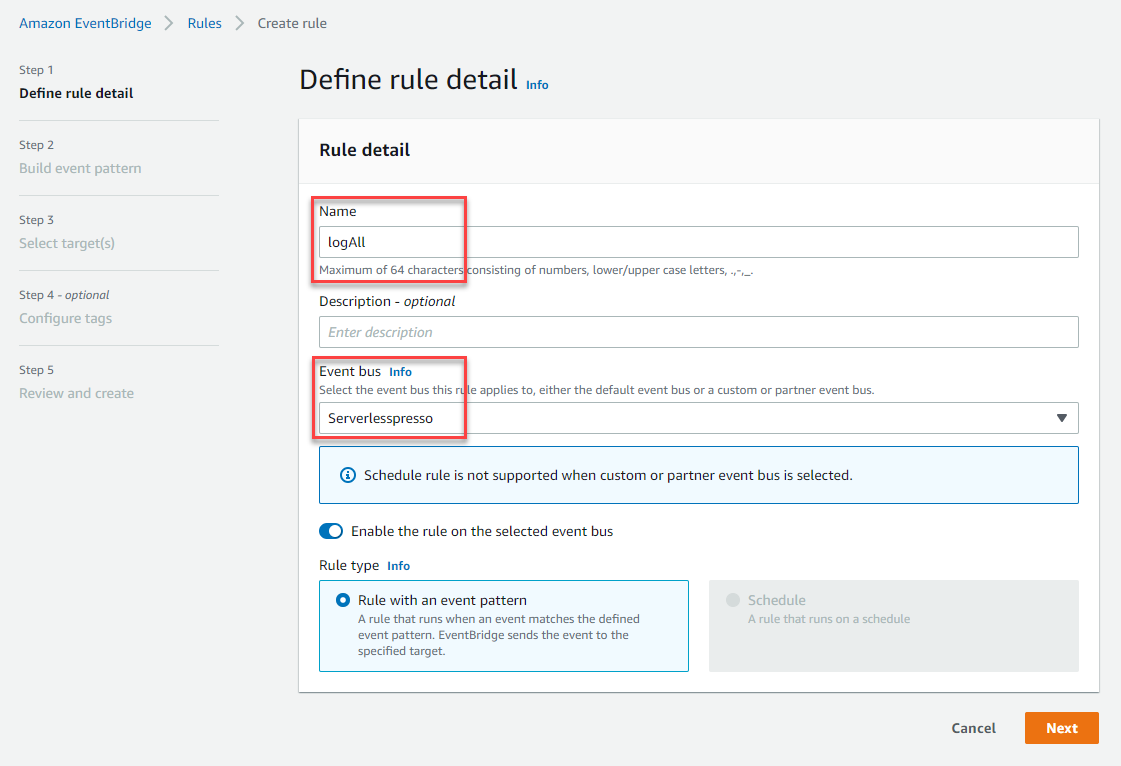
- In Step 1 of the wizard:
- For the Name, enter logAll.
- For Event bus, enter
Serverlesspresso. - Choose Next.
- In Step 2 of the wizard:
- For Event source, select Other.
- Ignore the Sample event panel.
- In the Event pattern panel, paste the following:
- Choose Next
{
"source": ["awsserverlessda.serverlesspresso"]
}
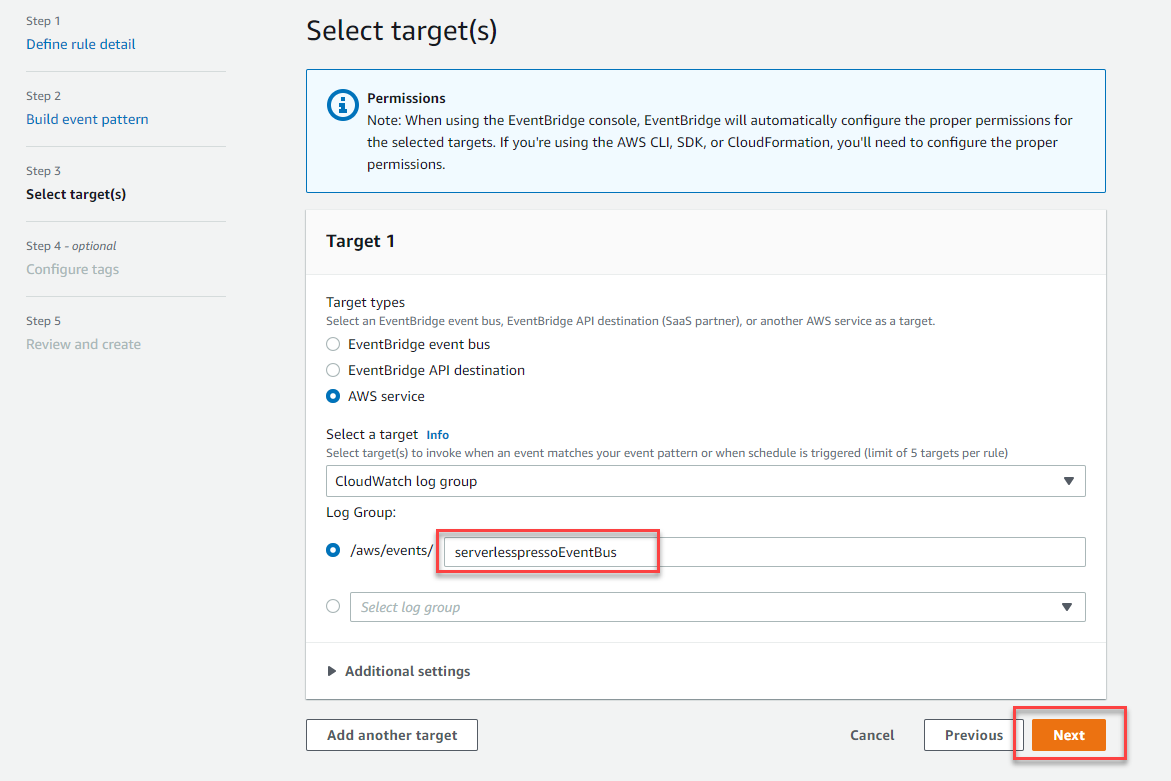
- In Step 3 of the wizard:
- In the Target 1 panel, choose AWS service.
- In the Select a target dropdown, choose CloudWatch log group
- In the Log Group field, enter serverlesspressoEventBus.
-
In Step 4 of the wizard, choose Next.
-
In Step 5 of the wizard, check that the Define rule detail panel that the Event bus is
Serverlesspresso. Choose Create rule.
Testing the “Log All” EventBridge rule
In this section, you will test that the rule logs all Serverlesspresso events to the correct log group. You use the Step Function workflow from module 1 to generate the events.
Step-by-step instructions
-
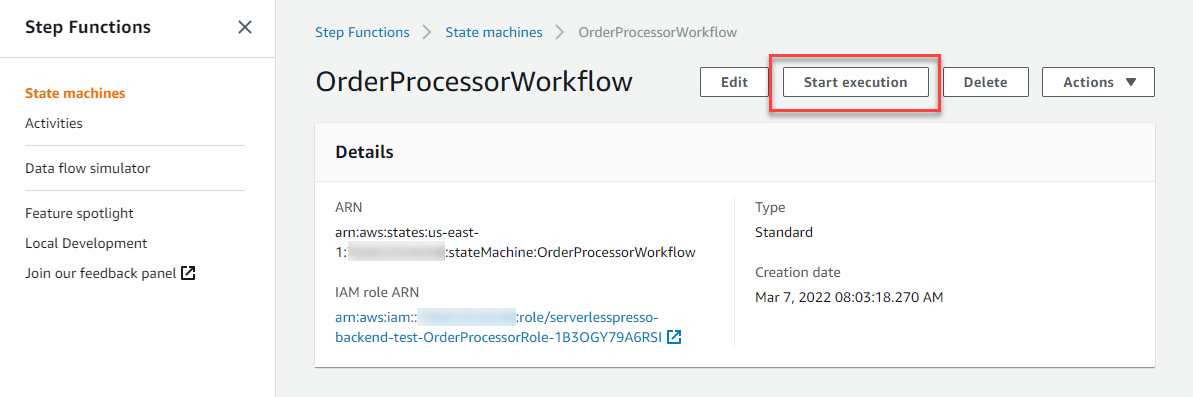
From the AWS Step Functions console, select the OrderProcessorWorkflow you created earlier.
-
From the section at top of the page showing the workflow, choose Start execution.
- In the Start execution pop-up, enter the following JSON payload in the Input textbox, then choose Start execution:
{
"detail": {
"orderId": "2",
"userId": "testuser2"
}
}
- The console shows the Execution status of Running. The left side shows the flow of execution with the green states showing the actual path. The blue state shows when execution is suspended, pending a callback.
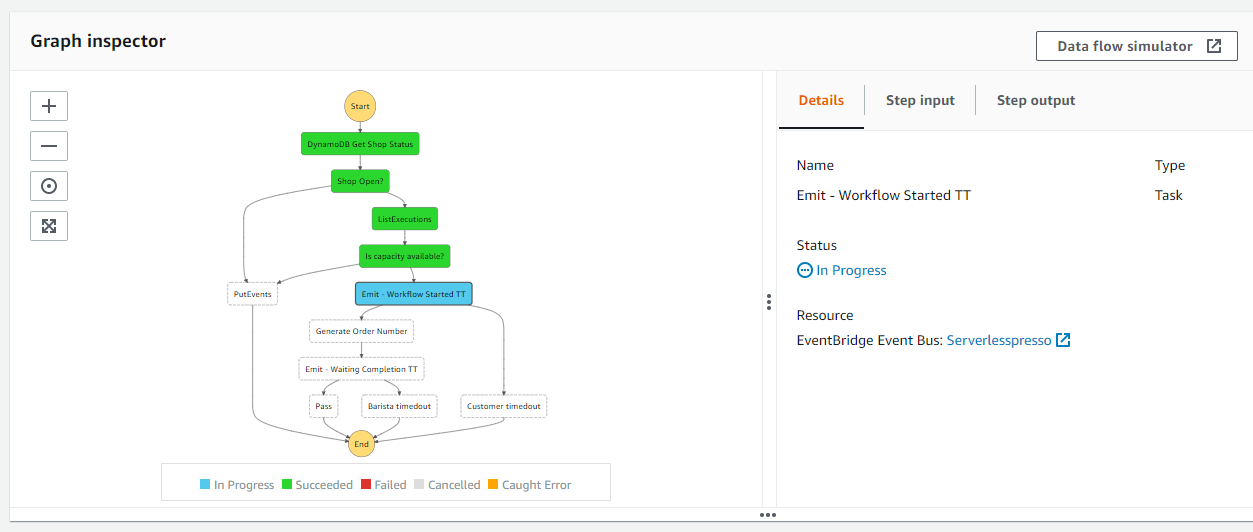
- In the Execution event history panel, open the TaskScheduled event for Emit - Workflow Started TT. This displays the payload for this event. The event detail information is also displayed here. It contains:
- The name of the event bus EventBusName that the event is emitted to (
serverlesspresso). - The event Source (
awsserverlessda.serverlesspresso). - The event
DetailType(OrderProcessor.WorkflowStarted).
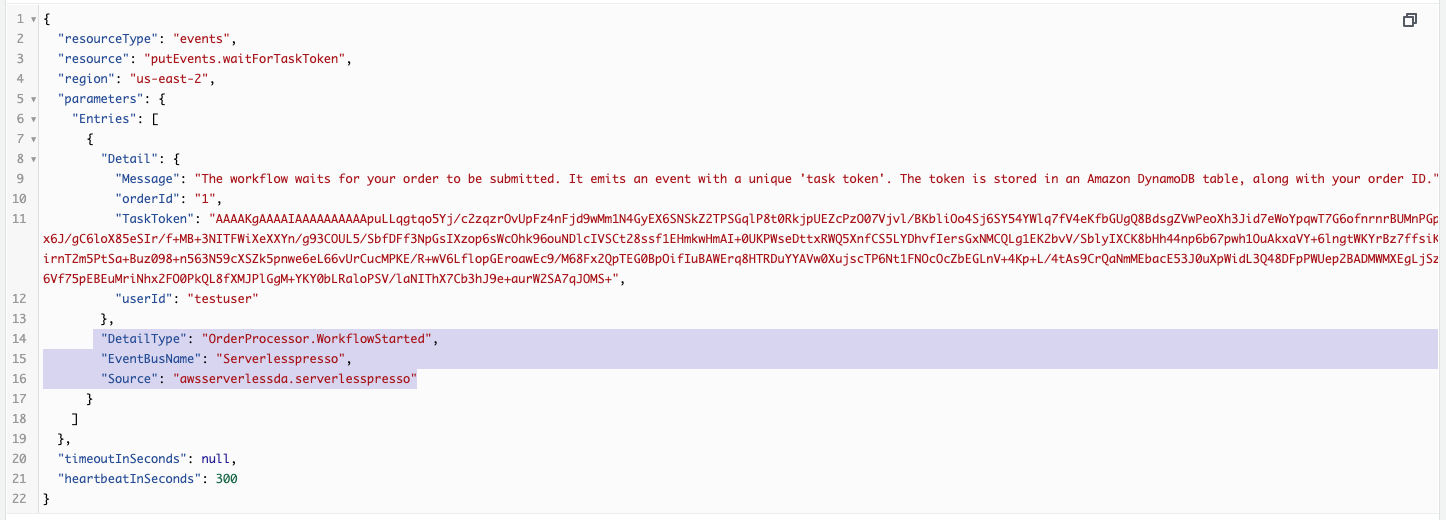
Since this event is emitted to the Serverlesspresso event bus and contains the source awsserverlessda.serverlesspresso, it is routed to CloudWatch Logs by the rule you created.
-
Go to the CloudWatch console. From the AWS Management Console, select Services then select CloudWatch in Management & Governance. Make sure your region is correct.
-
From the left menu, choose Log groups. Choose the log group called
/aws/events/serverlesspressoEventBus.
-
Each event is logged to a separate log stream. Choose the first log stream.
-
From the Target(s) section, choose the target named severlesspressoEventBus, then choose the first row in the Log Stream section. Expand the arrow next to the timestamp.
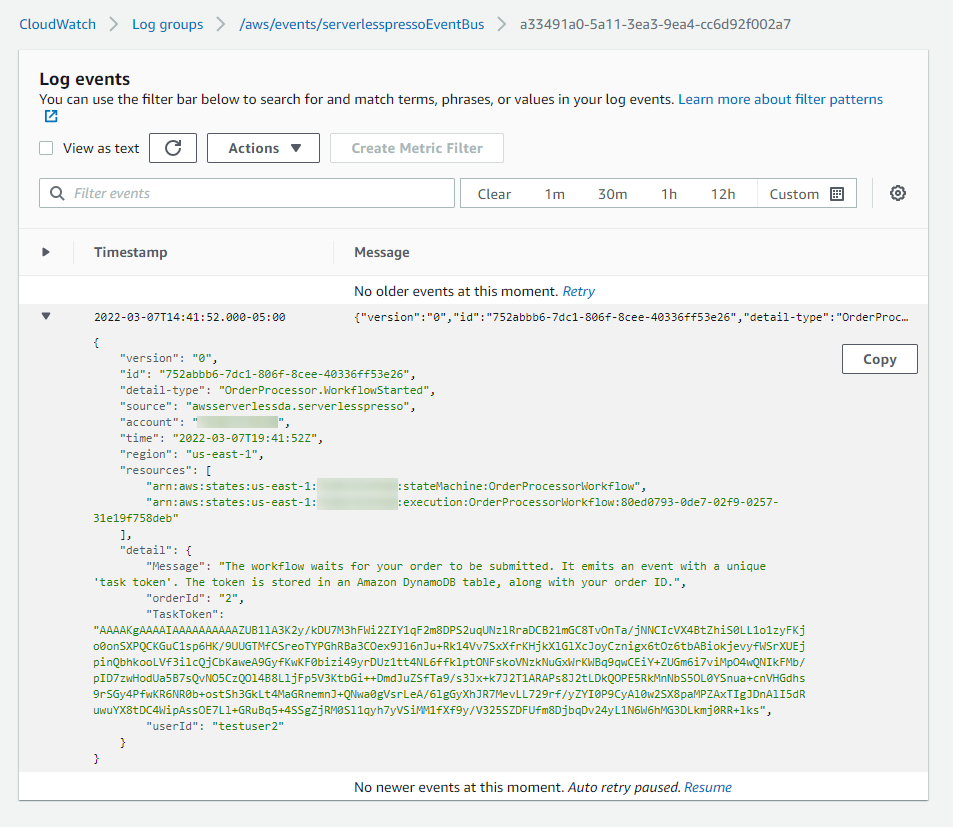
This shows all event information, including the TaskToken generated by Step Functions, the event detail-type, and the event source.
From now on, any event that is emitted to the Serverlesspresso custom event bus will be sent to CloudWatch Logs and available for inspection.
Recap
- For debugging purposes, it can be useful to log every event processed by a custom event bus. In this section, you created a catch-all rule that outputs every event to CloudWatch Logs.
- You generated a test event by running the workflow from module 1 and saw the logged event in CloudWatch Logs.
Next steps
Next, you’ll create a rule that routes events from the Validator service to the order workflow.