Workflow Started
Overview
The Order Processor workflow built in module emits the WorkflowStarted event. At this point in the order, the workflow has checked that the shop is open and that the barista has capacity for the new order. The workflow now waits for up to 15 minutes for the customer to choose and submit their coffee order. This is the first time in the process that the order waits for human interaction.
Step Functions does this by implementing the Wait for callback Task Token pattern. It passes the task token to the integrated service (Amazon EventBridge). The task pauses until the workflow receives that task token back with a SendTaskSuccess or SendTaskFailure call.
In the next step you create the rule that receives the WorkflowStarted event containing the task token. You route this event to an AWS Lambda Function which persists the token to an AWS DynamoDB table, along with the unique order ID.
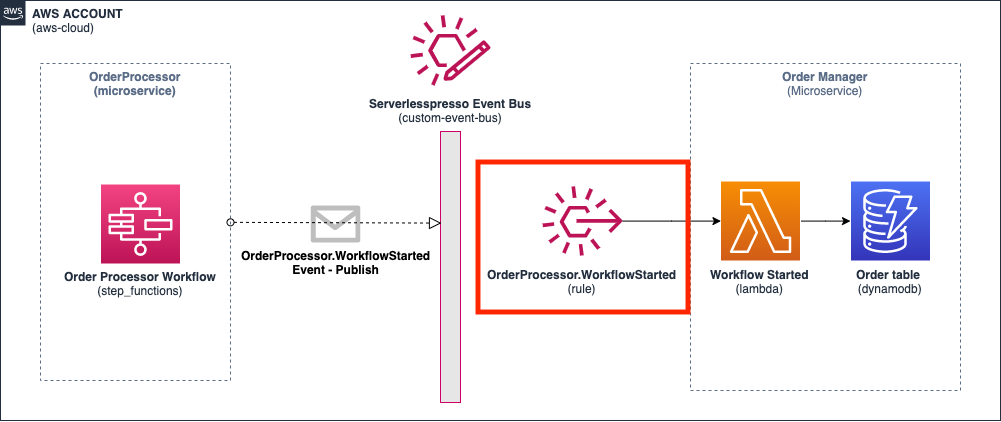
The Order Manager service keeps track of all the individual drink orders (e.g. “Double espresso”) and their completion status. The service is used by the Barista and Customer Apps to fetch lists of open or completed orders. This service is kept in sync by listening to events from the workflow.
In this section:
- You will create a new rule in Amazon EventBridge.
- You will configure the new rule to invoke an AWS Lambda Function.
- You will test the new rule and see the Lambda function input payload and response.
Creating the Workflow Started rule
Step-by-step instructions
-
Go to the EventBridge console. From the AWS Management Console, select Services then select EventBridge Application Integration. Make sure your region is correct.
-
Choose Rules. Choose Create rule.
-
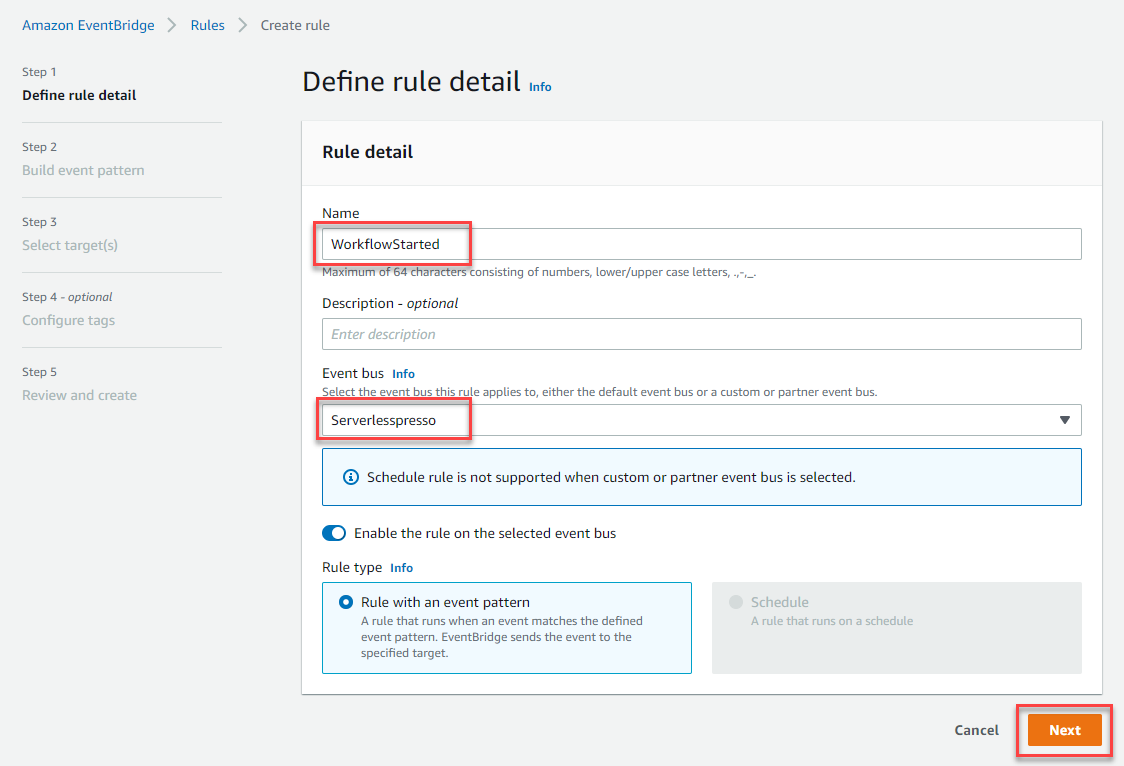
In Step 1 of the wizard:
- For the Name, enter WorkflowStarted.
- For Event bus, enter
Serverlesspresso. - Choose Next.
- In Step 2 of the wizard:
- For Event source, select Other.
- Ignore the Sample event panel.
- In the Event pattern panel, paste the following:
- Choose Next
{
"detail-type": ["OrderProcessor.WorkflowStarted"],
"source": ["awsserverlessda.serverlesspresso"]
}
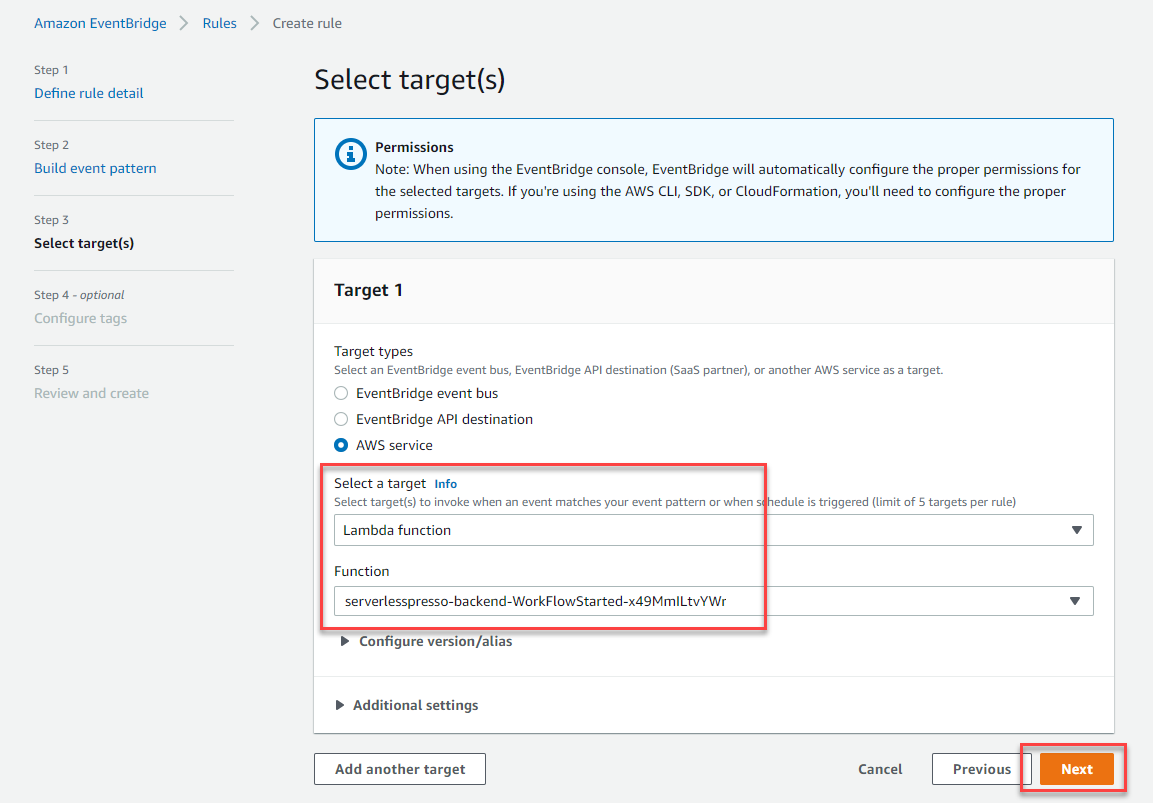
- In Step 3 of the wizard:
- In the Target 1 panel, choose AWS service.
- In the Select a target dropdown, choose Lambda
- In the Function dropdown, choose the Lambda function containing the name
WorkflowStartedfrom the Function dropdown. This was deployed by the core stack in the setup module. Tip: you can start typing “WorkflowStarted” into the field to find the function. - Choose Next.
-
In Step 4 of the wizard, choose Next.
-
In Step 5 of the wizard, check that the Define rule detail panel that the Event bus is
Serverlesspresso. Choose Create rule.
Testing the “WorkflowStarted” EventBridge rule
In this section, you will test that the rule invokes the WorkflowStarted Lambda function, and inspect the event payload and results.
Step-by-step instructions
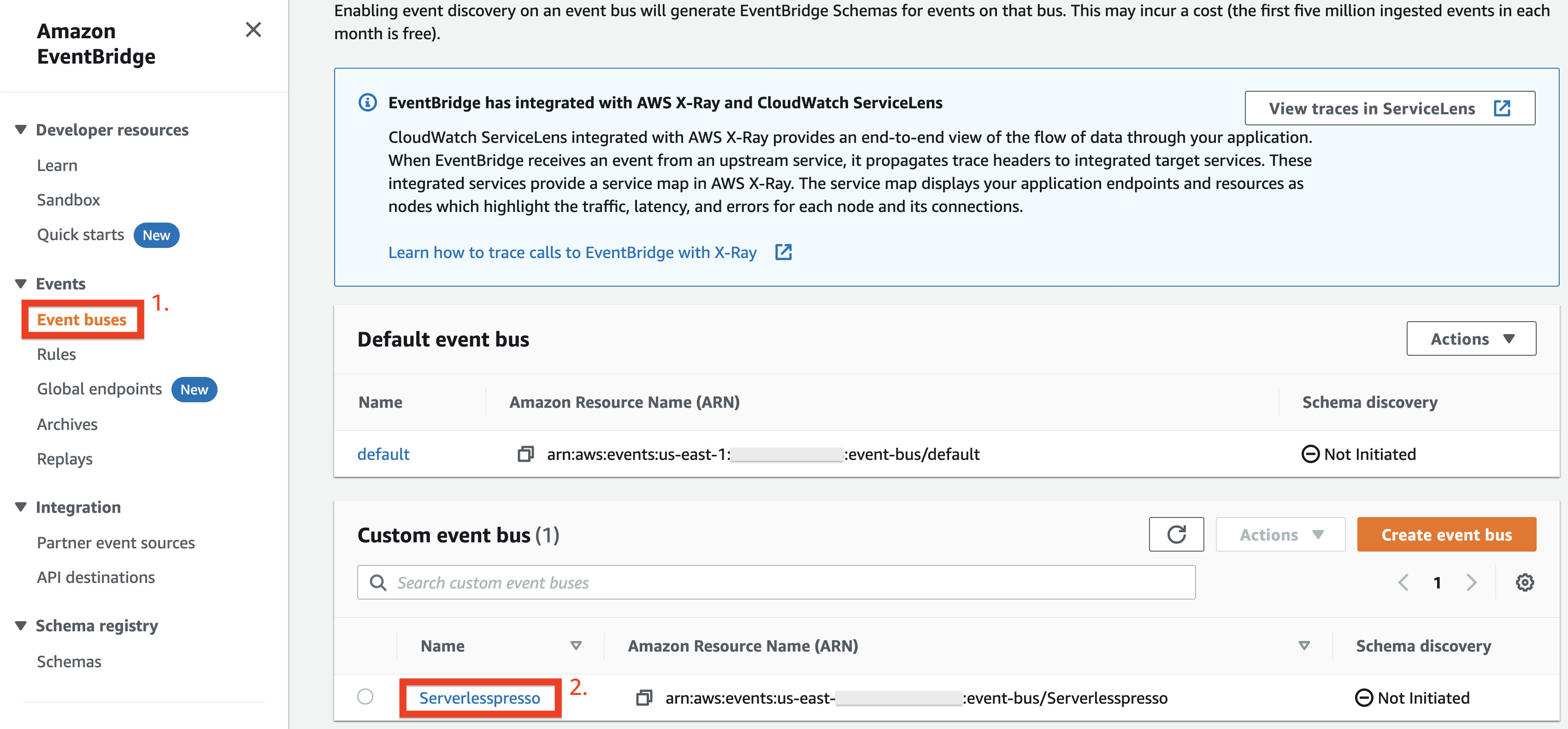
To start a new workflow, from the AWS EventBridge Console, under Events:
-
Choose Event busses.
-
Choose the Serverlesspresso event bus
-
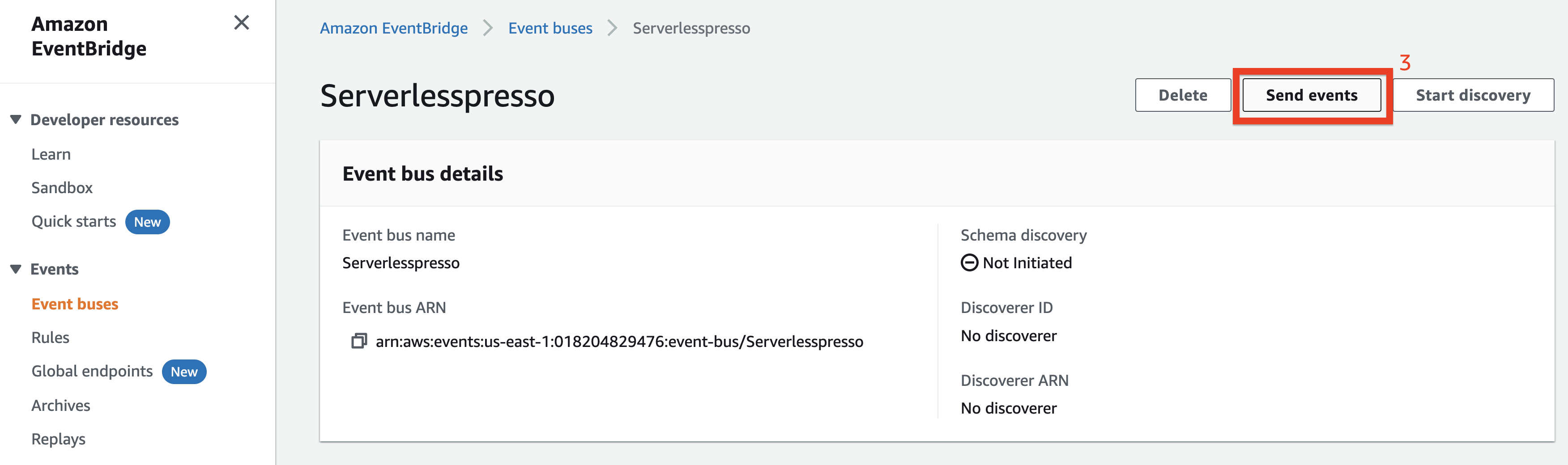
Choose Send events
-
Check that the serverlesspresso event bus is selected
-
Copy the following into the Event source input:
awsserverlessda.serverlesspresso
- Copy the following into the Detail type input:
Validator.NewOrder
- Copy the following into the Event detail input:
{"userId":"1","orderId":"1"}
- Choose Send
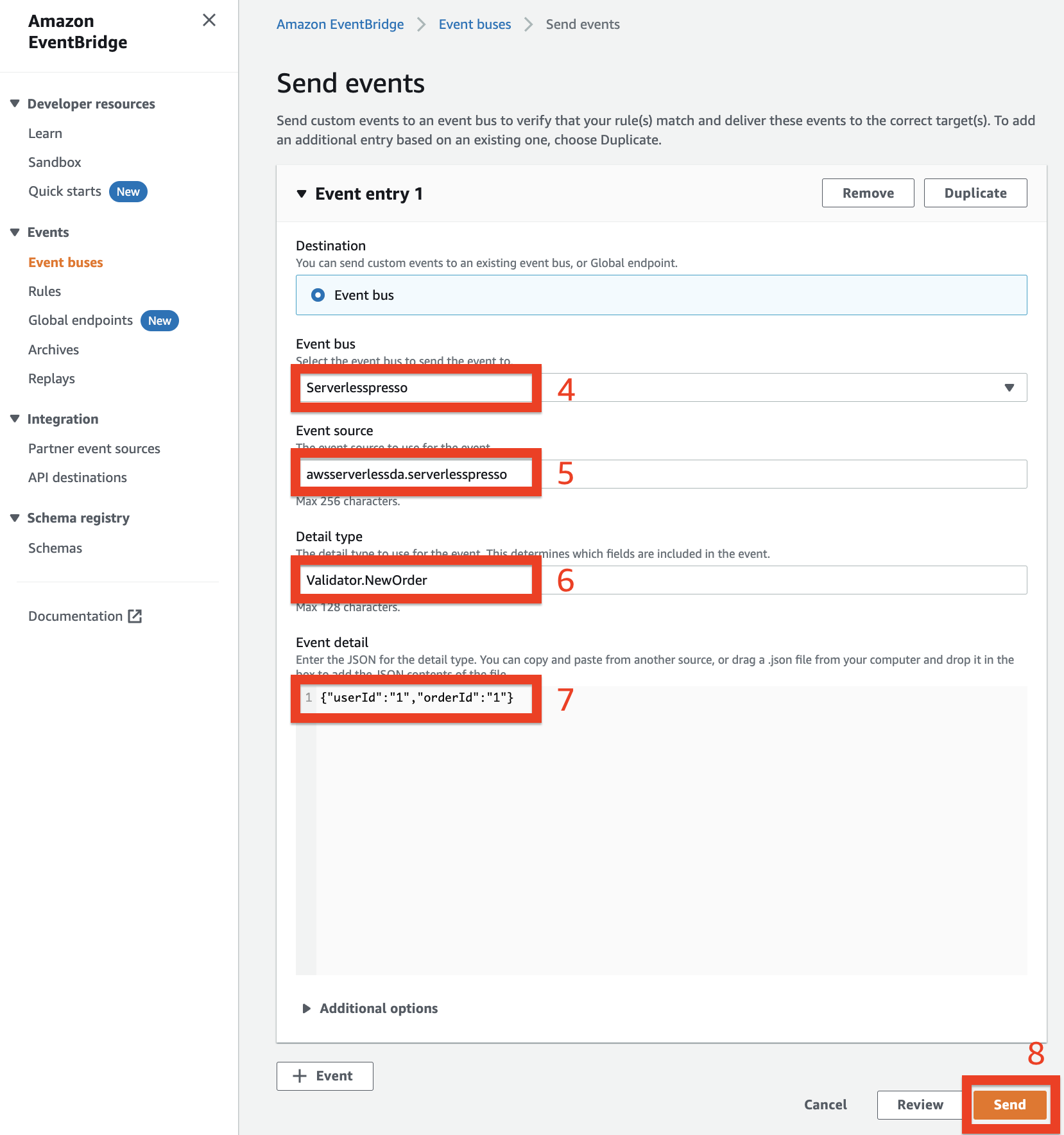
The rule you created called NewOrder triggers the OrderProcessor workflow. This in turn sends a WorkflowStarted event to the Serverlesspresso event bus.
-
Go to the CloudWatch console. From the AWS Management Console, select Services then select CloudWatch in Management & Governance. Make sure your region is correct.
-
From the left menu, choose Log groups. Choose the log group called
/aws/events/serverlesspressoEventBus.
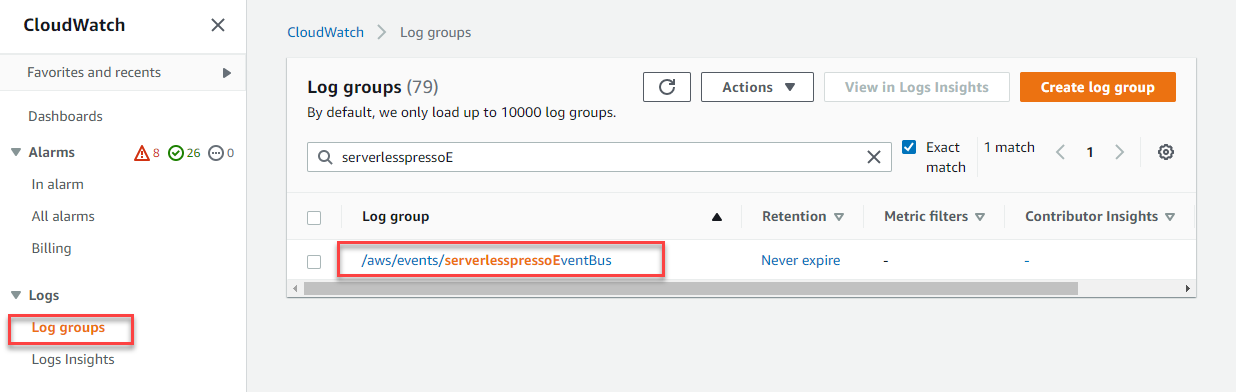
- The two most recent log streams shown contain the two events.
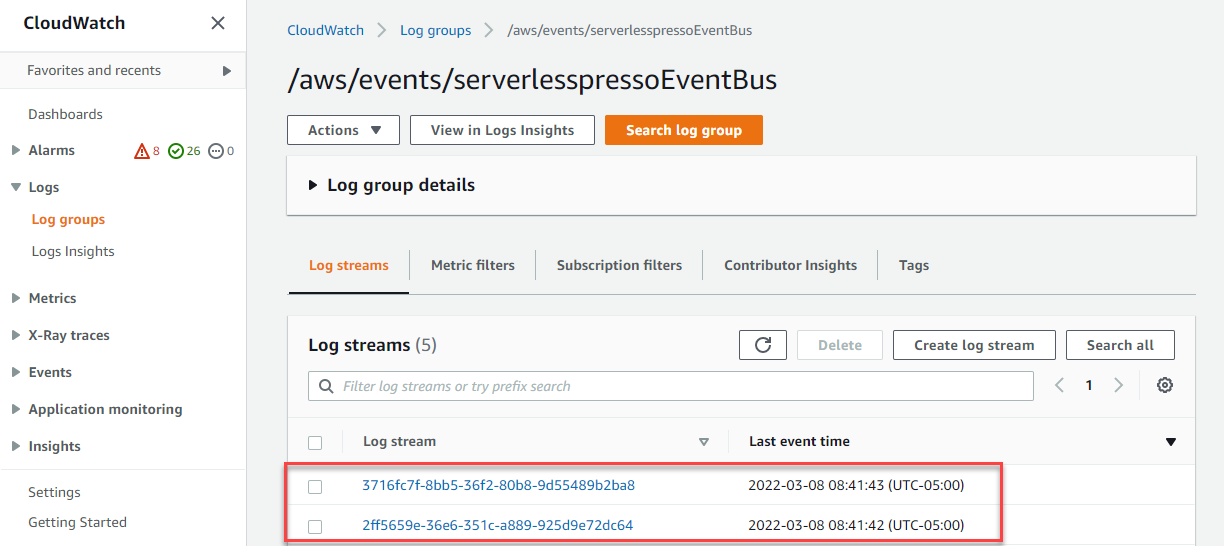
- Choose the most recent log stream to show the detail and expand the arrow next to the Timestamp column. This shows the
OrderProcessor.WorkflowStartedevent that was processed by the event bus.
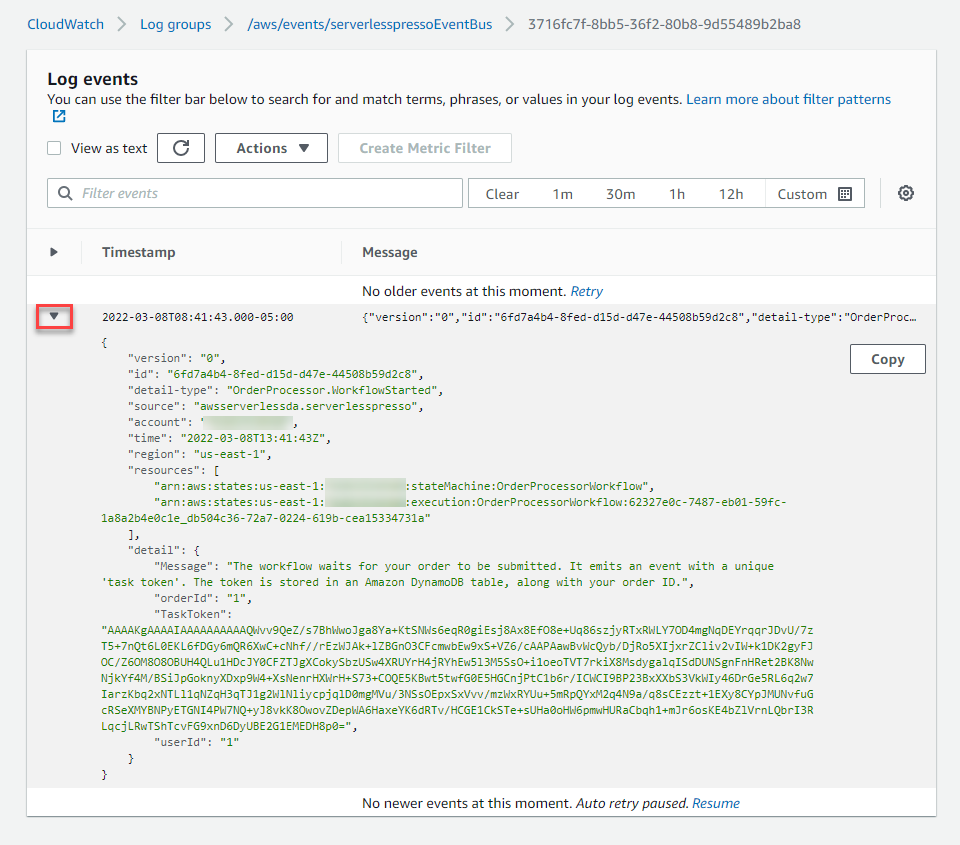
This shows all the event information, including the TaskToken generated by Step Functions, the event detail-type, and the event’s source.
-
The new WorkflowStarted rule has routed this event to the WorkflowStarted Lambda function. This Lambda function writes the task token to a DynamoDB table named serverlesspresso-order-table.
-
Go to the DynamoDB console. From the AWS Management Console, select Services then select DynamoDB in Database. Make sure your region is correct.
-
Select Explore items in the Tables menu on the left. Select the table
serverlesspresso-order-table.
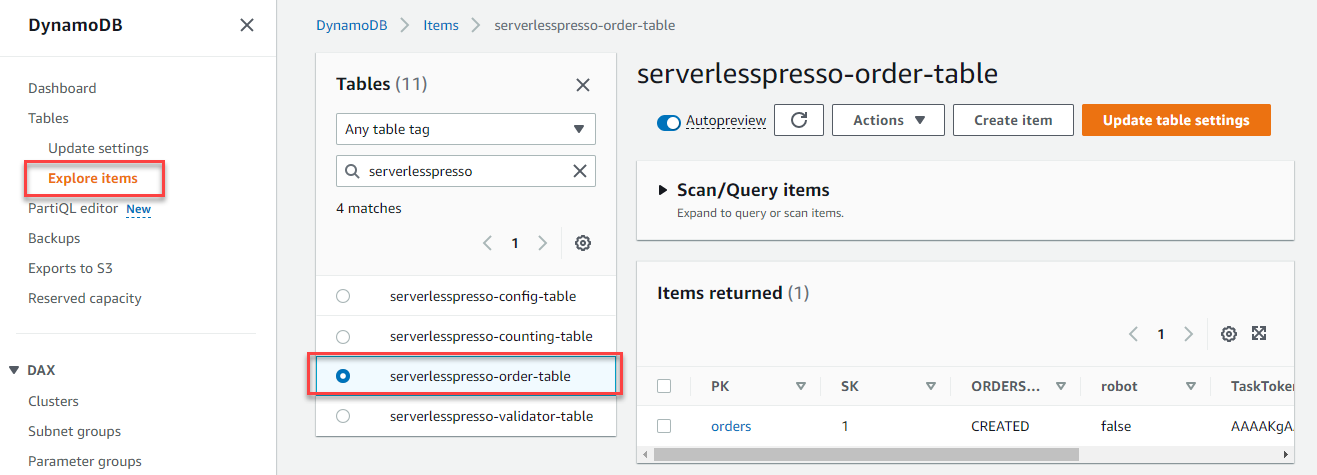
- In the Items returned panel, choose the first item to view its contents. The order was written to the DynamoDB table by the Lambda function. The item contains the Step Functions
TaskToken, the Order ID (“SK”), and the “ORDERSTATE”:
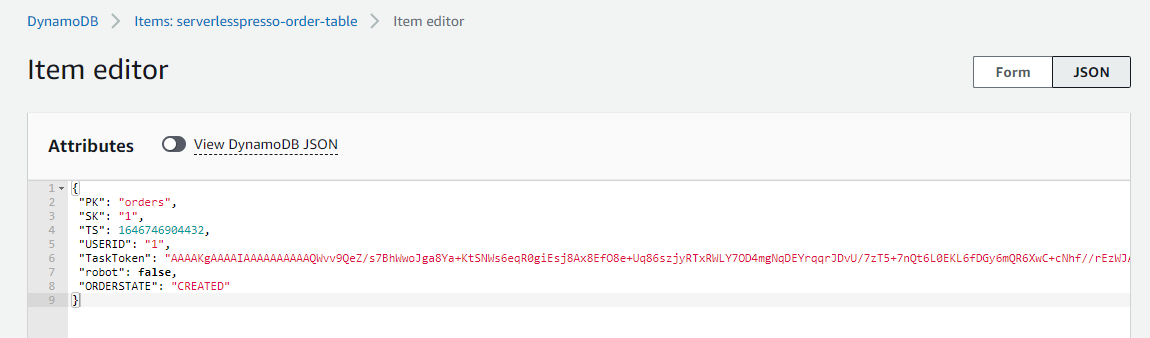
When the customer submits the drink order from the Customer App, the Order Manager microservice will fetch this task token from DynamoDB and return it to the Step Functions service. This is then used to resume the workflow for that order.
In the next section you will see how orders are canceled, updated, and completed by a separate workflow called the OrderManager
Recap
- You created a new rule to invoke a Lambda function that writes order information to a DynamoDB table.
- You tested by mocking an event from the CLI, observing the events processed by the custom event bus, and verifying that the order information is written to the DynamoDB table.
Next steps
Congratulations! You have configured rules to process events and deliver selected events to different targets. This connects backend microservices together when events occur throughout the workload. In the next section, you will use the three frontend applications to test the backend.